Invoice lifecycle
Overview
In accounts receivable, an invoice is a type of receivable issued by a company to its customers for delivered goods or used services that have not been paid for yet. This usually occurs because of credit sales and as a result of buying goods or services on credit.
Monite API enables the whole accounts receivable aspect of SME’s business to run in an “auto pilot” mode. By integrating Monite API to your software or any other application:
- Creating and sending invoices becomes much more convenient.
- Follow-up (such as invoice payment reminders and overdue reminders) is fully automated.
- Transparency (“where do we stand” and “what do I need to do”) is always given.
Invoice statuses
Outgoing invoices move through different statuses from the time they are created to when they are paid.
Monite API provides a flexible invoice workflow to be managed by each entity and their respective entity users. The entities can easily control access to invoices based on the role assigned to each employee through the user hierarchy.
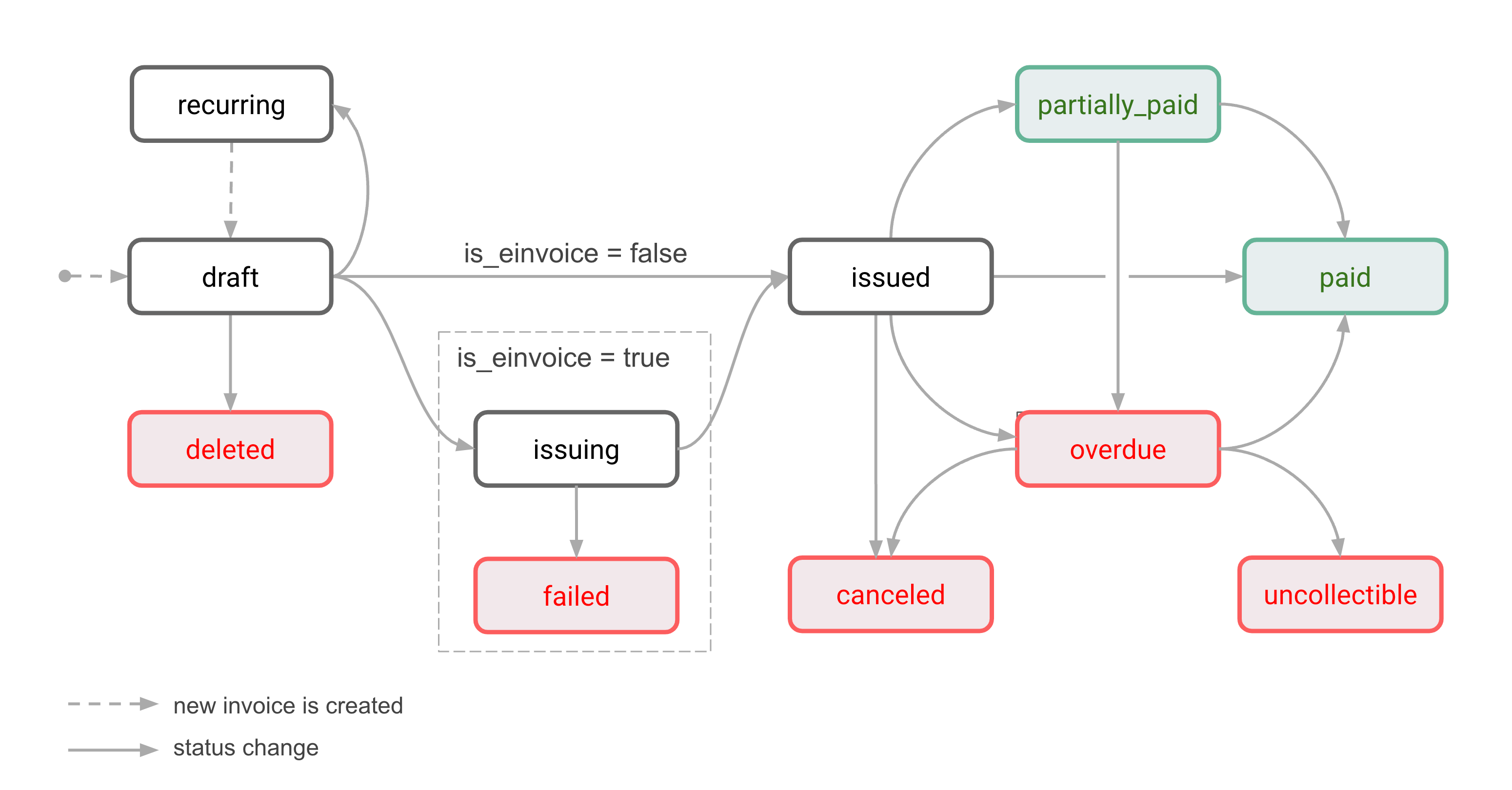
Draft
All newly created invoices have the draft status. A draft invoice has not yet been finalized and issued, and can be edited at any time.
Draft invoices are the only ones that can be deleted.
Issuing
An invoice is moved to this status when it is submitted to an e-invoicing network.
If the e-invoice is successfully sent, the status becomes issued, otherwise it becomes failed.
Failed
This status indicates an error from an e-invoicing network.
E-invoices that failed to be sent cannot be resent. It is a final status.
Issued
Indicates that the invoice has been finalized and issued to the counterpart. If e-invoicing is used, this status means the invoice was successfully sent to the counterpart via the e-invoicing network.
Issued invoices cannot be edited or deleted, just canceled.
Recurring
When configuring recurring invoices, the recurring status is assigned to the base invoice from which the recurring invoices will be generated. The recurring invoices themselves go through the normal receivable lifecycle (such as draft → issued → paid).
Even if the recurrence ends or is canceled, the base invoice remains with the recurring status.
Paid
The paid status indicates that the customer has fully paid the invoice and the entity has received the funds on its bank account. This is the final state of an invoice.
An invoice can reach the paid status in several ways:
- The customer pays the invoice via a payment link or an embedded payment component. In this case, Monite changes the invoice status to
paidautomatically after the payment has settled. - The entity records an invoice payment for the remaining invoice amount.
- The entity marks the invoice as paid directly.
If the entity setting generate_paid_invoice_pdf is true, once an invoice becomes paid its PDF version is automatically updated to reflect the paid status:
-
entity bank account details for payments are removed,
-
the payment amount block displays two additional lines:
Partially paid
An invoice gets this status when a partial payment is recorded for this invoice. The counterpart will continue receiving payment reminders (if they are configured) until the invoice is paid in full.
If the counterpart pays the remaining amount by the due date, the invoice status is changed to paid. Issuing a credit note for the remaining amount also marks the invoice as paid.
Partially paid invoices cannot be canceled or deleted, but can become overdue if not fully paid by the due date.
A partially paid invoice that is overdue has the overdue status rather than partially_paid.
If the entity setting generate_paid_invoice_pdf is true, the totals block in the PDF invoice includes a list of all payments made and credit notes applied, for example:
Overdue
Indicates that the counterpart has not paid the invoice in full by the due date. Depending on the commercial conditions, the counterpart will or will not be able to make further payments against the invoice. Overdue reminders can be sent if needed.
If the counterpart pays an overdue invoice in full, the invoice status becomes paid.
An overdue invoice cannot be deleted, but it is possible to cancel the invoice or mark it as uncollectible to write it off.
Canceled
An entity can cancel an invoice, for example, if it contains incorrect information or was issued by mistake. Only issued and overdue invoices that have not been paid in full can be canceled. A partially paid invoice can be canceled if it is overdue. The counterpart cannot make payments towards a canceled invoice.
Depending on the entity settings, canceling an invoice can automatically issue a credit note for the remaining invoice amount.
Canceled invoices cannot be deleted and remain in the system for accounting purposes. This is a final status.
For more information, see Cancel an invoice.
Deleted
Only draft invoices can be deleted. Deleted invoices can no longer be accessed.
For more information, see Delete an invoice.
Uncollectible
Indicates that the counterpart is unlikely to pay this invoice.
The difference between uncollectible and canceled is that uncollectible still has a legal claim on the counterpart. Uncollectible is also a final state after handing over an invoice to a debt collection agency that was not able to retrieve the funds. For bookkeeping, this is a write off and has a tax implication.
For more information, see Mark an invoice as uncollectible.